- Understanding Schema Markup and Its Importance for SEO
- Markup Formats Explained: Choosing the Right Syntax for Your Website
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Adding Schema Markup to Your Site
- 4 Steps to Implement Schema Markup on Your Website
- 6 Benefits of Using Schema Markup for Your Website's Visibility.
- 6 Advanced Techniques for Maximizing the Impact of your schema.org implementation.
- Conclusion: Harness the Power of Schema Markup to Improve Your Website's
Understanding Schema Markup and Its Importance for SEO
Schema markup, also known as structured data, plays a crucial role in optimizing websites for search engines. It provides additional information to search engines about the content on a webpage, making it easier for them to understand and index the page accurately.
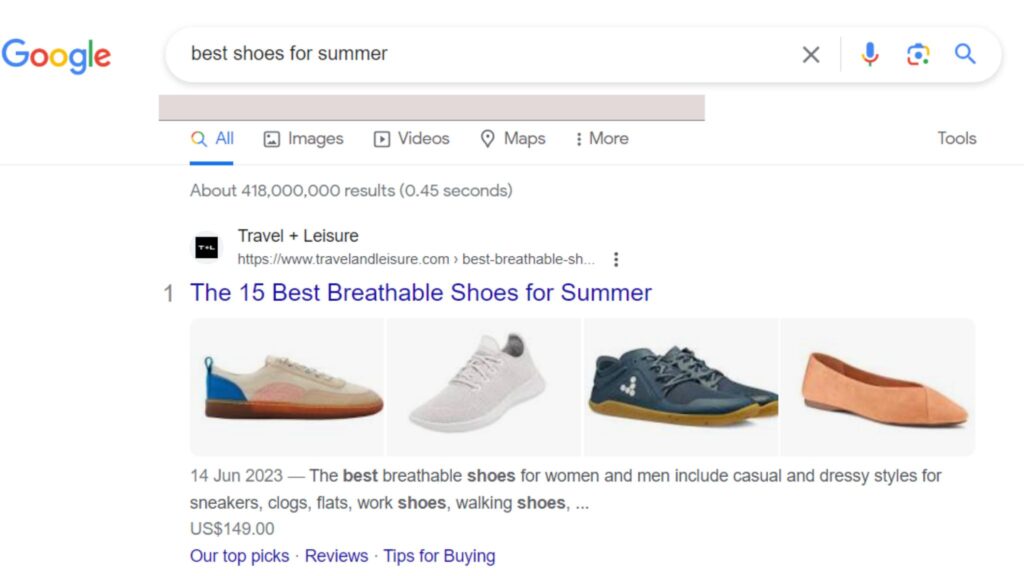
By implementing schema markup, website owners can enhance their website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). This is because search engines like Google use structured data to create rich snippets, which are more informative and visually appealing than regular search results.
Rich snippets often include additional details! Such as ratings, reviews, prices, and other relevant information that can attract users’ attention and increase click-through rates.
Furthermore, schema markup helps search engines better understand the context of the content on a webpage. This enables them to display more targeted and relevant results to users.
Websites with properly implemented schema markup are more likely to rank higher in search engine rankings for specific queries.
In summary, incorporating schema markup into a website’s code is essential for SEO optimization. It not only improves website visibility but also increases the chances of attracting organic traffic from users actively searching for related products/services.
By providing search engines with structured data about your content, you can improve your website’s chances of ranking higher in SERPs. Ultimately driving more targeted traffic to your site.
Worthknowing about Markup: How It Works
There are different formats of schema markup, including microdata, RDFa, and JSON-LD. These formats allow webmasters to add schema markup directly into their HTML code.
Microdata involves adding specific HTML attributes to the existing code, allowing search engines to identify and extract relevant information from the page.
RDFa is another format that uses HTML5 attributes to define structured data within a webpage. JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is a script-based format that separates the structured data from the HTML code.

Schema.org provides a wide range of schema types that can be used depending on the type of content being marked up. These schema types include events, products, recipes, organizations, reviews, and many more.
Markup Formats Explained: Choosing the Right Syntax for Your Website
Markup formats play a crucial role in organizing and structuring information on websites. Providing a standardized way to communicate with search engines and other applications, helping them understand the content and context of web pages.
One popular markup format is schema syntax, which allows you to define specific elements on your website using predefined tags.
Schema syntax, also known as schema markup or structured data, uses a vocabulary of tags based on schemas defined by Schema.org. These tags provide additional information about different types of content, such as articles, products, events, recipes, and more.
Choosing the right schema syntax for your website depends on various factors such as the type of content you have, your target audience, and your specific goals.
As I earlier mentioned, Schema.org provides a wide range of schemas to cover different industries and content types.
Some common schema syntaxes include JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data), RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes), and Microdata.
JSON-LD is widely considered the recommended format by Google due to its simplicity and compatibility with modern web development practices. It allows you to add structured data directly into the head section of your HTML code using JavaScript objects. RDFa is another popular choice that allows you to embed structured data within HTML attributes.
Microdata is an older method that uses HTML attributes to mark up content but requires more effort compared to JSON-LD or RDFa. However, it still remains compatible with most search engines.
When choosing the right schema syntax for your website, consider factors such as ease of implementation, compatibility with search engines’ recommendations (especially Google). Also, consider support from popular content management systems (CMS). Not forgetting availability of resources or plugins that assist in implementing schema markup.
Implementing schema markup may seem daunting at first glance; however, it offers numerous benefits. Including improved search engine visibility, enhanced click-through rates, and richer search results.
By choosing the right schema syntax for your website and implementing it correctly, you can make your content more accessible. You also make it relevant, and appealing to both users and search engines alike.
Anatomy of a Schema Markup: Key Elements and Attributes to Include
Schema markup is a powerful tool! It helps search engines understand the content on your website in a more structured and meaningful way.
To effectively implement schema markup, it’s important to understand its key elements and attributes. Let’s dive into the anatomy of a schema markup and explore the essential components you should include.
- Schema Type: The first step is to select the appropriate schema type that best represents the content on your webpage. There are various types available, such as Article, Event, Product, Organization, Local Business, and many more. Choosing the right schema type ensures that search engines interpret your content accurately.
- Properties: Within each schema type, there are specific properties or attributes that provide additional information about your content. For example, an Article schema type may include properties like headline, description, author name, publication date, image URL, and so on. These properties help search engines categorize and display your content appropriately in search results.
- Microdata Markup: To implement schema markup on your webpage accurately, you need to use microdata—an HTML attribute that includes specific tags. This is to indicate which parts of your content correspond to different aspects of the chosen schema type. These tags should be placed within relevant HTML elements such as headings or paragraphs.
- Structured Data Testing: After implementing the schema markup on your webpage using microdata tags, it’s crucial to test its validity using structured data testing tools provided by major search engines like Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool or Bing’s Markup Validator. These tools help identify any errors or warnings in your implementation and ensure that search engines can interpret it correctly.
- Continuous Monitoring: As with any technical implementation on a website, monitoring is essential for maintaining optimal performance. Keep an eye on changes in search engine guidelines related to schema markup. And regularly test the validity of your markup to ensure it remains up-to-date and error-free.
Understanding these key elements and attributes of a schema markup can help you effectively leverage this tool to provide search engines with structured data about your content. This, in turn, can increase the visibility and relevance of your website in search results.
Additive vs. Replacement Approach: Implementing Schema on Existing Web Pages
The additive approach involves adding Schema markup to your existing HTML code without altering the structure or content of your web pages. This means you can simply insert the necessary Schema markup alongside your existing content.
This approach is ideal if you want to enhance the search engine visibility of your pages without making significant changes to their layout or design. By adding Schema markup, you provide search engines with valuable information about your content. Hence, making it easier for them to understand and index your pages.
On the other hand, the replacement approach involves modifying your existing HTML code to incorporate Schema markup directly into the structure of your web pages. This approach requires more extensive changes as you’ll need to replace or restructure certain elements of your content to accommodate the Schema markup. While this may require more effort upfront, it can offer greater benefits in terms of search engine optimization and semantic understanding.
Choosing between these two approaches depends on your specific goals and resources. If you have limited time or technical expertise, the additive approach may be more suitable! Because it allows you to quickly implement Schema markup without significant modifications.
However, if you’re willing to invest more time and effort into optimizing your web pages for search engines, the replacement approach can provide a more comprehensive solution.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Adding Schema Markup to Your Site
When adding schema markup to your site, it’s important to avoid common mistakes that can hinder its effectiveness. Here are some mistakes to steer clear of:
- Incorrect implementation: One of the most common mistakes is not implementing schema markup correctly. Make sure you follow the schema.org guidelines and use the appropriate markup for each type of content on your site. Incorrectly implemented markup can confuse search engines and lead to inaccurate or incomplete results.
- Overusing markup: While it’s important to include schema markup where relevant, overusing it can be counterproductive. Don’t add markup to every element on your page just for the sake of it. Focus on marking up the most important and relevant information to give search engines a clear understanding of your content.
- Ignoring updates: Schema.org regularly updates its vocabulary, adding new types and properties. It’s crucial to stay up-to-date with these updates and make any necessary changes to your schema markup. Ignoring updates can result in outdated or incorrect information being displayed in search results.
- Inconsistent schema implementation: Ensure that your schema markup is consistent across all pages of your site. Inconsistencies in how you apply schema can confuse search engines and affect how your site is indexed. Maintain a cohesive schema implementation strategy throughout your site.
- Lack of testing: Before deploying schema markup on your live site, it’s essential to test it thoroughly. Use structured data testing tools provided by search engines to identify any errors or issues with your markup. Testing allows you to catch mistakes early on and ensure that your schema is correctly interpreted by search engines.
- Neglecting non-visible content: Schema markup is not limited to visible elements on your website. It can also be added to non-visible content such as metadata, embedded videos, or audio files. Neglecting to include schema markup in these areas can result in missed opportunities for enhanced search engine visibility.
- Not monitoring performance: After implementing schema markup, it’s crucial to monitor its performance. Keep an eye on your site’s search engine rankings, click-through rates, and overall organic traffic. This data will help you evaluate the effectiveness of your schema markup and make any necessary adjustments.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your schema markup enhances the visibility and understanding of your website’s content. Take the time to implement schema correctly, stay updated.
4 Steps to Implement Schema Markup on Your Website
- Identify the Key Pages and Content Types to Markup with Schema
- Find the Right Schema Markup Generator or Plugins for Your CMS (Content Management System)
- Add Your Schema Markup to Your Webpages Using HTML or CMS Plugins
- Validate and Test Your Schema Implementation for Errors or Missing Elements

6 Benefits of Using Schema Markup for Your Website’s Visibility.
There are several key benefits of using Schema Markup on a website. Below are some I find to be the most notable ones:
- Improved search engine visibility: Schema Markup helps search engines understand the content on your website more effectively. By providing structured data, search engines can display rich snippets in search results, which can increase visibility and attract more visitors to your site.
- Enhanced click-through rates: With Schema Markup, you can display additional information in search results such as reviews, ratings, prices, and availability. These rich snippets can make your listing stand out from competitors and entice users to click on your website over others, improving your click-through rates.
- Better user experience: Schema Markup allows you to provide more detailed information about your products, services, and business. Users can quickly grasp essential details without even visiting your site, improving the overall user experience and helping them make informed decisions.
- Increased local search prominence: For businesses with physical locations, Schema Markup can help improve local search visibility. By adding schema tags specific to your location (such as address, phone number, opening hours), search engines can provide accurate and authoritative local business information to potential customers.
- Competitive advantage: Although Schema Markup is not yet widely adopted across all websites, implementing it correctly can give you a significant advantage over competitors who haven’t utilized this technique. By providing search engines with structured data, your website becomes more visible and trustworthy, standing out in the search results.
- Future-proofing your website: As search engine algorithms evolve and become more sophisticated, structured data will likely play a more significant role in determining rankings and search results presentation. By implementing Schema Markup now, you’re future-proofing your website and staying ahead of the curve.
6 Advanced Techniques for Maximizing the Impact of your schema.org implementation.
- Cross-referencing Multiple Schemas for Richer Search Results Representation.
- Including User Reviews and Ratings in Product Schemas.
- Utilizing Event Schemas to Promote Events and Drive Attendance.
- Showcasing Recipes with Rich Snippets in Food & Recipe Blogs.
- Incorporating Local Business Information with Location and Contact Schemas.
- Enhancing Job Postings with Structured Data Markup.
Conclusion: Harness the Power of Schema Markup to Improve Your Website’s
I firmly believe implementing schema markup on your website can have a tremendous impact on its visibility and search engine optimization. By providing search engines with structured data, you enable them to better understand your content and display it in a more relevant way to potential visitors.
Not only does schema markup help improve the appearance of your website in search results, but it also enhances the overall user experience. So, if you’re looking to maximize your website’s visibility and attract more targeted traffic, don’t overlook the power of schema markup.
Start implementing this valuable tool today and watch your website’s visibility soar above the competition.
A prominent SEO and Business Analyst with 5+ years of experience helping businesses achieve growth